Test Environment:
LinuxDevelopment Environment: Yocto 5.0(scarthgap)
U-Boot: U-Boot 2024.04
Kernel: Linux-6.6.36
Linux SDK: L6.6.36-2.1.0
Version: Debix SOM A V1.01_20241024
Devices: 2 * DEBIX SOM A + DEBIX SOM A IO Board
Test Steps:
1. Power on and run 2 pcs of mainboards, then enter the device console.
2. Run DebixVersion to check the basic information of the device.
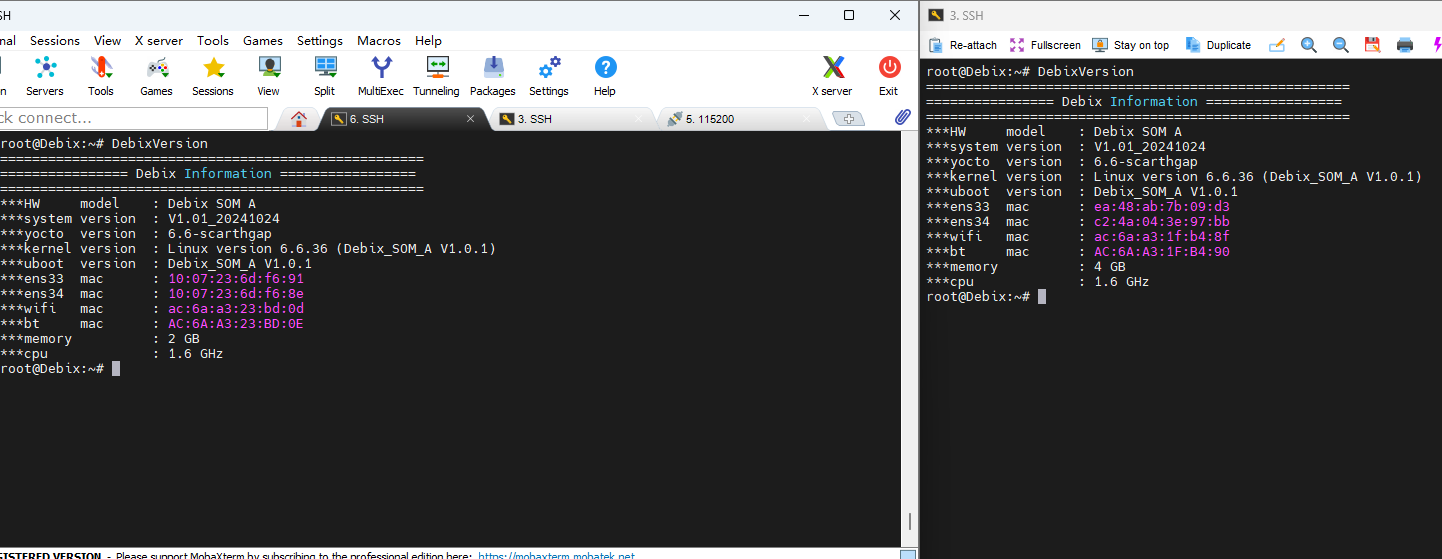
3. Connect the ETH1 interfaces of the two DEBIX SOM A IO Boards using an Ethernet cable (only ETH1 supports TSN, you can check with the command ethtool -T ens33).
4. On the master device console, run:
ptp4l -E -4 -H -i ens33 -l 6 -m -q -f /etc/linuxptp/ptp4l.conf
5. On the slave device console, run:
ptp4l -E -4 -H -i ens33 -s -l 6 -m -q -f /etc/linuxptp/ptp4l.conf
6. Check the printed log information.
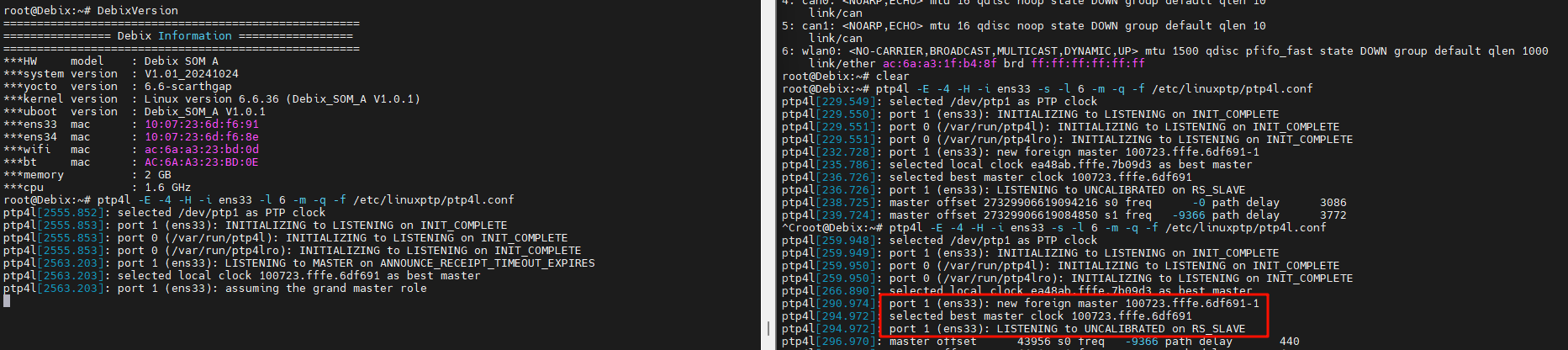
7. The log shows that the slave device synchronizes with the external master clock 100723.fffe.6df691-1, which corresponds to the master device’s ETH1 port.
8. Once the test stabilizes, review the data.
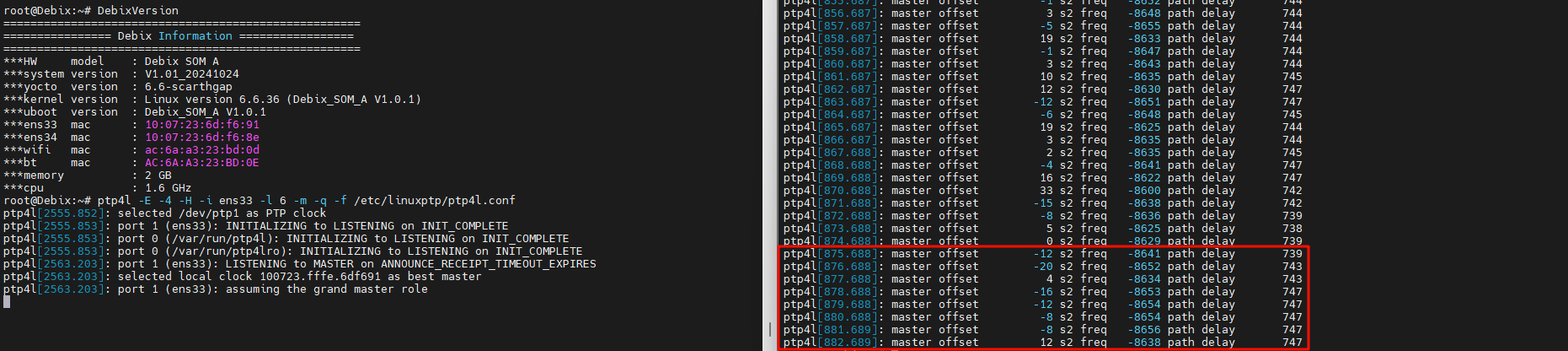
9. Example of the last log entry:
ptp4l[882.689]: master offset 12 s2 freq -8638 path delay 747
l ptp4l[882.689]
² ptp4l: This is the core daemon implementing the PTP (Precision Time Protocol) on Linux. PTP, also known as IEEE 1588, is a high-precision time synchronization protocol designed to provide sub-microsecond synchronization for devices within a LAN.
² [882.689]: Process runtime timestamp in seconds, showing elapsed time since the process started.
l master offset: 12
Meaning: The time difference between the local clock (slave) and the remote master clock.
Unit: Nanoseconds (ns).
Interpretation: 12 means the local clock lags behind the master clock by 12 ns. This is extremely precise synchronization (1 second = 1,000,000,000 ns).
l s2 freq: -8638
Meaning: The frequency adjustment value calculated by ptp4l to correct clock offset in slave state. s2 refers to the slave state of ptp4l.
Unit: Parts per billion (ppb). This value will be passed to phc2sys (used to synchronize the system clock and hardware clock) or directly to the Linux kernel clock discipline.
Interpretation: -8638 means the local oscillator frequency is reduced by 8638 ppb to catch up with the master. This relatively large adjustment indicates the local clock was initially faster.
l path delay: 747
Meaning: The round-trip delay between slave and master.
Unit: Nanoseconds (ns).
Interpretation: 747 ns is very low, suggesting excellent network hardware performance (likely hardware timestamping support). In software-timestamped networks, this value is usually tens to hundreds of microseconds.
Explanation of Test Command Parameters
Parameter
Function
Description
-E
Delay mechanism
Use end-to-end (E2E) delay measurement.
-4
Network stack
Use only IPv4 addresses.
-H
Timestamping
Enable hardware timestamping (critical for high accuracy).
-i
Interface
Specify the network interface used for PTP communication (in this example: ens33).
-l
Log level
Set the verbosity level of log messages (in this example: 6 = INFO level).
-m
Log output
Print logs to standard output for viewing.
-q
Quiet mode
Suppress periodic sync messages. (e.g., log master offset)。
-f
Config file
Read configuration from the specified file (in this example: /etc/linuxptp/ptp4l.conf).
-s
Clock mode
Run as slave and synchronize with master (slave only).












